Asymmetries can make all the difference…
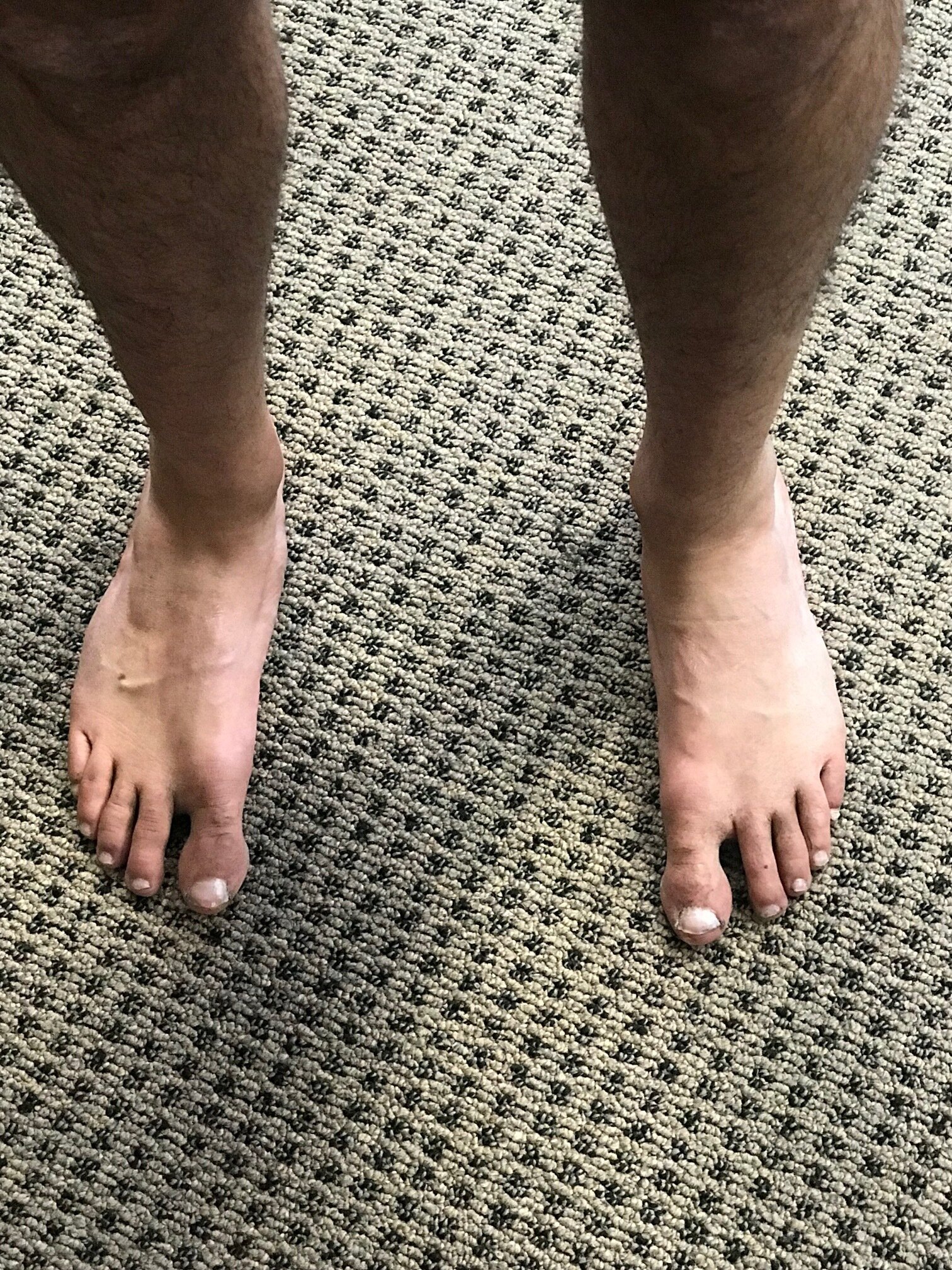
/Take a good look at these pictures of this gentleman’s feet. Can you see any differences from side to side?
If you look closely, you’ll notice that his right foot is in and abducted position (4 foot adductus) and relatively normal. Asymmetries can make all the difference…
Take a good look at these pictures of this gentleman‘s feet. Can you see any differences from side to side?
If you look closely, you will notice that his right foot is in an adducted position (forefoot adductus) and the left one relatively normal. If you bisect the heel, it should pass through the second or between the second and third metatarsal in his clearly falls laterally.
So what you say?
Well, putting a foot in relative supination with respect to the other causes certain biomechanical sequela. This forefoot adductus often leads to a forefoot supinatus, so he’s unable to get the head of his first ray down to the ground. Think that might make a difference in his gait cycle?
Think about all the extra internal rotation that will have to occur in that lower extremity during a normal gait cycle. Now combine that with something like external tibial torsion or a leg length discrepancy and things can really stack up and make a big difference.
Lastly, think about the asymmetrical mechanoreceptor input from the joint mechanoreceptors and muscle spindles traveling up the neuraxis. Do you think over time that that may cause some cortical remodeling and ultimately change the way he activates muscles?
Look for asymmetries, they really do matter
Dr Ivo Waerlop, one of The Gait Guys
#asymmetriesmatter #gaitanalysis #thegaitguys #forefootadductus